What is Pulmonary AVM Embolization?
“Pulmonary” refers to the lungs. A pulmonary arteriovenous malformation (or “AVM”) is an abnormal connection of blood vessels in the lungs. This abnormal connection can make it difficult to breathe or do activities. Pulmonary AVMs can also cause serious bleeding in the chest. They can also lead to strokes or brain infections. These risks are greater if the abnormal connection is large or you have more than one AVM.
Embolization is a minimally invasive way to treat the abnormal connection of vessels by blocking them with special material. This allows blood to flow only through the normal remaining vessels in your lungs.
How is Pulmonary AVM Embolization done?
You will be given medication to help you relax. The skin on your groin or wrist will be cleaned then numbed. The clinician will thread a small plastic tube through a pinhole in the skin into a blood vessel. They will use x-rays and dye to guide them as they move the tube through your vessels to the AVM in your lungs. They will inject special material through the small tube into the abnormal connection to stop blood from flowing through it. After, they remove the tube then put a bandage over the pinhole where the tube entered your skin.
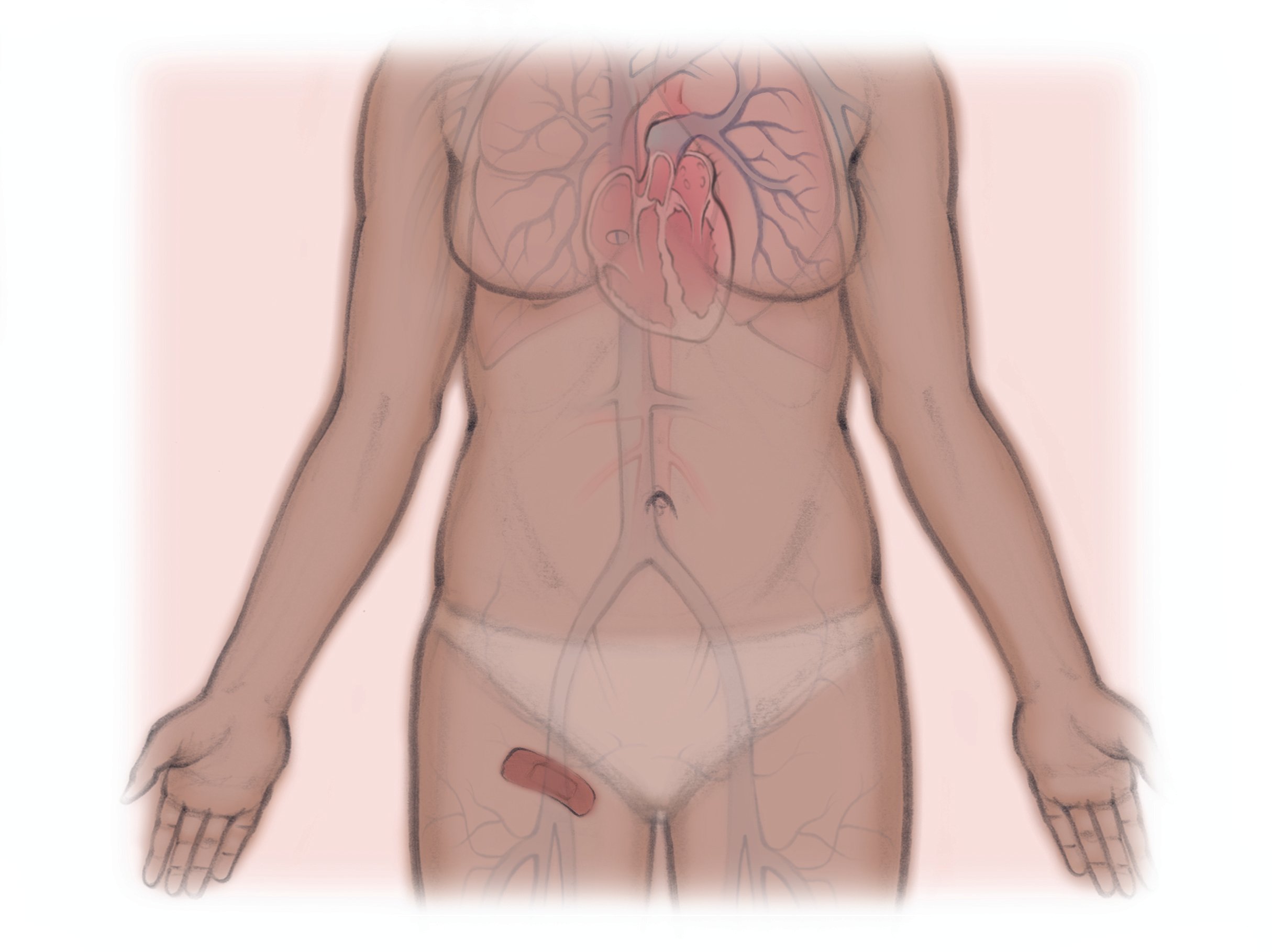
Pulmonary AVM Embolization
1. After numbing the skin, the clinician slides a small tube into the blood vessel at the top of the thigh or wrist.
2. The clinician uses x-rays and dye to guide the tube through the body to the AVM. Then, they inject special material to block the AVM.
3. After, the clinician removes the tube and places a bandage over the pinhole in the skin.
What are the risks?
Pulmonary AVM embolization is generally a safe procedure when done by a specialist
15 in 100 people experience chest pain. It is more common with larger AVMs and generally goes away on its own.
In less than 1 in 100 people, the special material goes somewhere unintended and
causes a stroke
damages a small part of the lung
What are the alternatives?
Your treatment options depend on your preferences, overall health and unique conditions.
Alternative 1 Not to treat the AVM. The advantage is that you avoid a procedure. The disadvantage is that you remain at risk for serious bleeding, stroke, and brain infection, which can be life-threatening.
Alternative 2 Surgery to block or cut out the abnormal connection of vessels. This can be successful but has much higher risks than embolization.