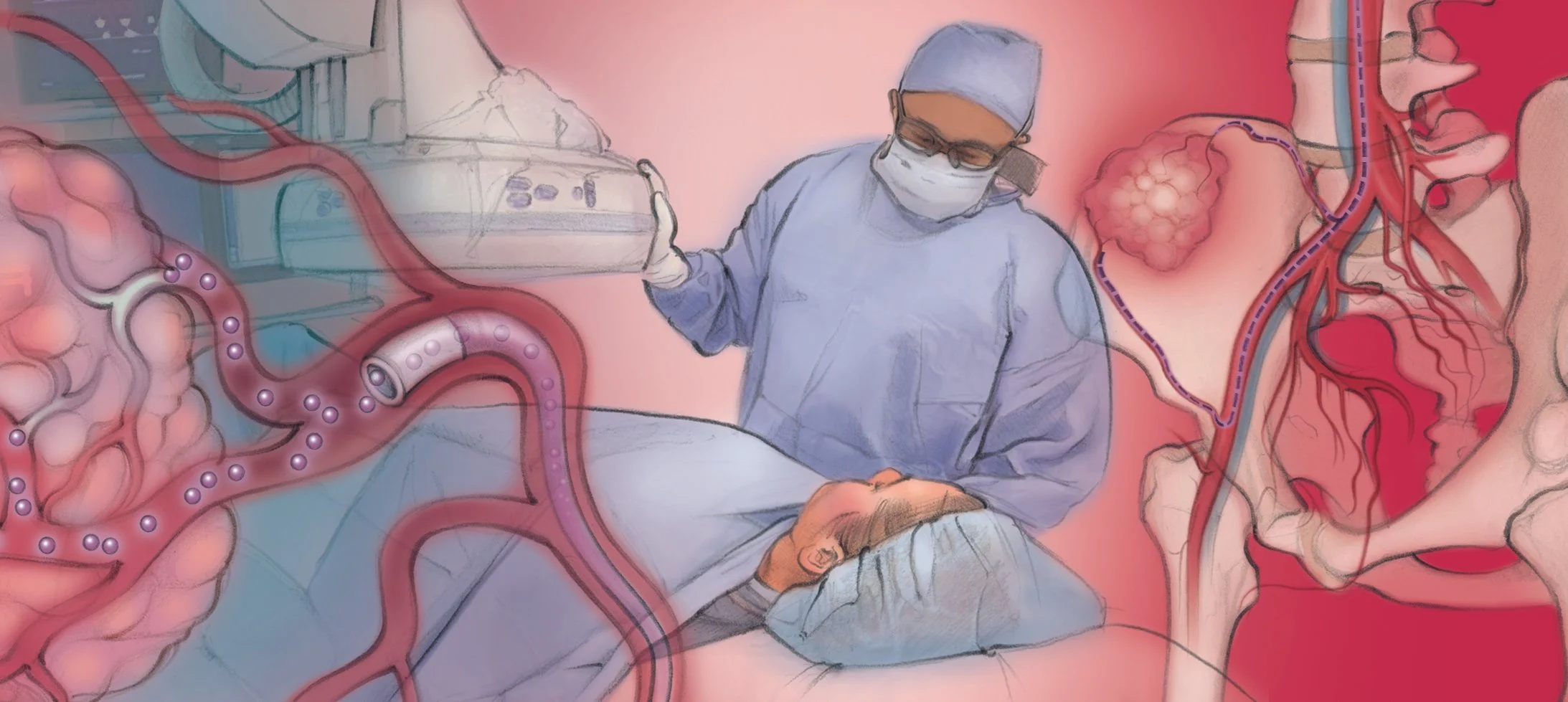
What is Preoperative Mass Embolization?
Preoperative mass embolization is a minimally invasive procedure performed to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery to remove a mass or tumor. It involves blocking off some of the blood vessels supplying the tumor or mass to reduce bleeding. This is called embolization.
How is Preoperative Mass Embolization done?
You will be given medicine to relax. The skin on your wrist or top of the thigh will be cleaned and numbed. The clinician will thread a thin tube through a pinhole in the skin into a blood vessel. They will use moving x-rays to guide the tube through the body to the vessels supplying the mass. They will inject special material to block those vessels. They will remove the tube and put a bandage over the pinhole where the tube entered the skin.
Preoperative Mass Embolization
1. After numbing the skin, a small tube is placed into the blood vessel at the top of the thigh (shown) or wrist.
2. The clinician guides it to the blood vessel that supplies the mass or tumor and then injects special material to block the blood vessel.
3. After, the clinician removes the tube and places a bandage over the pinhole in the skin.
What are the risks?
Embolization of a mass or tumor is generally a safe procedure when done by a specialist.
Most people have some pain at the mass. Sometimes people experience fever, fatigue, and nausea for a few days after embolization. These symptoms are temporary and can usually be managed with medicines.
Other risks are bleeding, damage to the blood vessels, infection, and accidental blockage of other blood vessels not supplying the mass. The specific risks depend on the size and location of the tumor(s) being embolized.
What are the alternatives?
Your treatment options depend on your preferences, overall health and unique conditions.
The main alternative is having surgery without embolization beforehand. The advantage of this is avoiding an additional procedure. The disadvantage is that you may lose more blood during surgery. This may require blood transfusions. It can also make the surgery much more difficult and increase the risk of complications.